Automation in PCB Assembly: The Big Picture
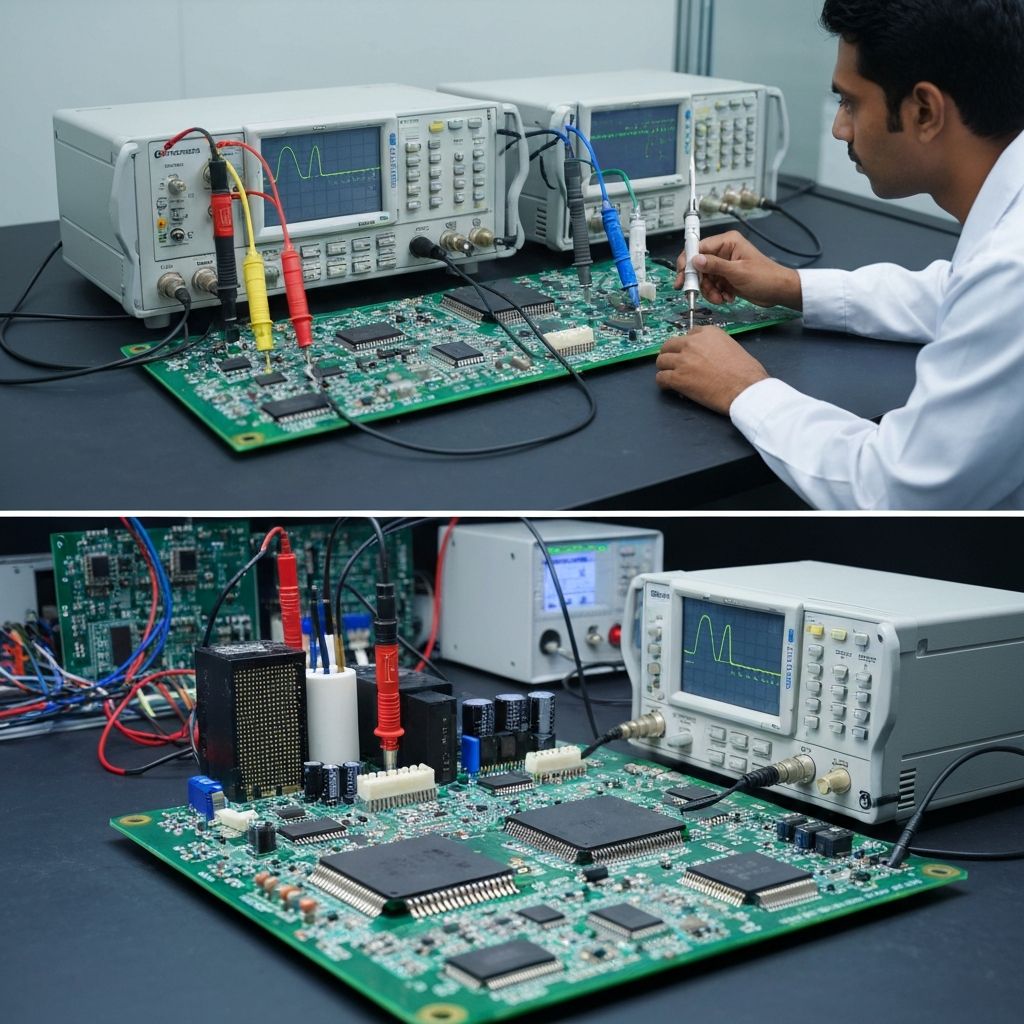
PCB assembly lines have evolved from semi-manual processes to highly automated, data-driven production systems. Today’s factories combine SMT machines, inspection systems, and MES/ERP integrations to deliver faster and more consistent output.
Trend 1: Higher-Speed SMT Lines
Modern pick-and-place machines can handle:
- Very small components (01005, micro-BGAs)
- High placement rates while maintaining accuracy
- Automatic reel changeovers and feeder optimizations
Trend 2: Intelligent Reflow Profiling
Reflow ovens now support advanced profiling and closed-loop control. Benefits include:
- Stable solder joints across varying PCB designs
- Reduced risk of tombstoning and voids
- Energy-efficient oven operation
Trend 3: AOI and SPI Integration
Solder Paste Inspection (SPI) and AOI are increasingly integrated into the line, enabling:
- Real-time process feedback on paste volume and placement quality
- Automatic adjustments to print parameters
- Early detection of defects before reflow
Trend 4: Industry 4.0 and Data Analytics
PCB assembly machines now generate rich data that can be analyzed for:
- Predictive maintenance of equipment
- Yield tracking by product, shift, or component
- OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) optimization
Trend 5: Flexible Automation for Mixed-Volume Production
With more product variants and shorter life cycles, EMS providers are investing in flexible automation:
- Quick-change fixtures and feeders
- Modular production cells
- Robotic material handling and labeling
Conclusion
Automation in PCB assembly is no longer optional — it is a competitive necessity. By choosing EMS partners who invest in modern equipment and data-driven processes, you gain better quality, consistency, and scalability for your products.